Table of Contents
Spotlight on African Innovators highlights startups across Africa tackling local challenges through cutting-edge solutions. In our last issue, we showcased seven transformative ventures revolutionizing sectors such as research, e-commerce, healthcare, arts, and logistics. Look out for our upcoming edition on December 5, 2025.
This edition introduces seven promising African startups operating in health, research, aquaculture, finance, and funding, each poised to make significant impacts. Let’s explore their stories:
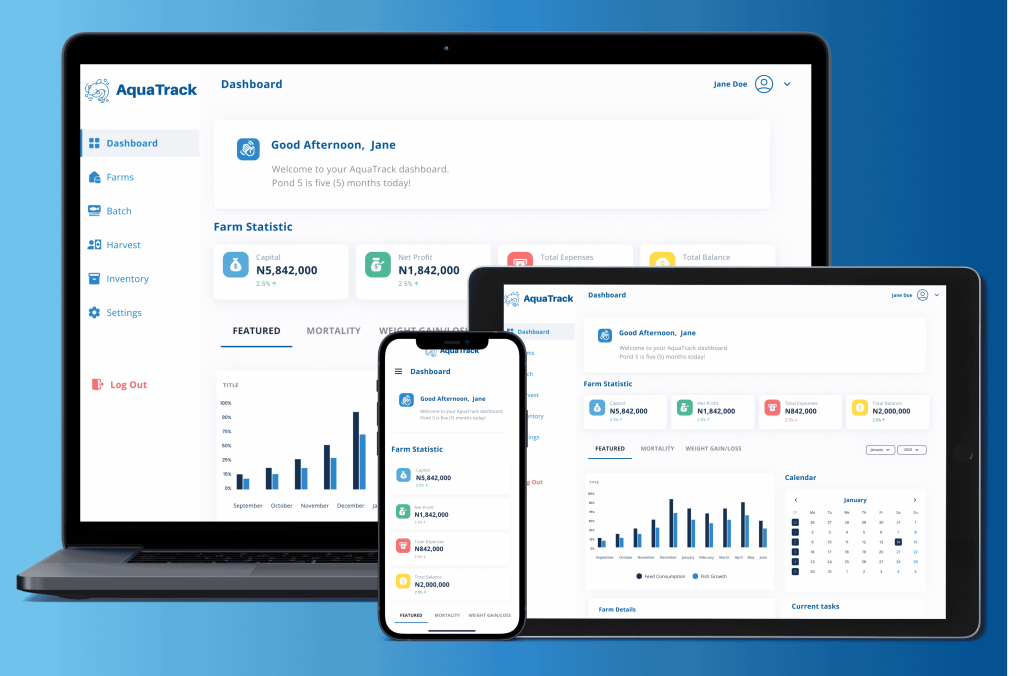
Revolutionizing Aquaculture: AquaTrack’s AI-Driven Farm Management (Agritech, Nigeria)
Sisters Deborah and Busola Falope founded AquaTrack after confronting firsthand the challenges of fish farming in Port Harcourt, including low productivity, high mortality rates, limited financing, and volatile markets. Their solution is an AI-powered platform that streamlines aquaculture management while connecting farmers to financial services and direct market access.
Accessible via a web app, AquaTrack enables farmers to oversee pond conditions, record feeding and mortality rates, and monitor stock lifecycles comprehensively. A harvest module facilitates real-time sales tracking, calculating profits, expenses, and capital flow.
Complementing the platform is an AI assistant available both in-app and through WhatsApp, designed to support farmers with limited tech skills by answering queries and extracting data from uploaded receipts. AquaTrack also partners with undisclosed financial institutions to provide credit access and operates an online seafood marketplace that links producers directly to consumers, eliminating intermediaries.
Since its 2024 launch and revenue generation starting January 2025, AquaTrack has onboarded over 1,000 farmers, facilitated sales exceeding 30 tons of fish across Bayelsa, Aba, Enugu, and Oyo, and processed transactions worth ₦23 million (~$15,850). The startup has also built a pipeline of more than 160,000 prospective users.
Why AquaTrack stands out: Unlike competitors such as Kenya’s Aquarech, which focus mainly on e-commerce, AquaTrack offers an integrated platform combining farm management, operational analytics, market linkage, and financing. Upcoming features include a predictive analytics tool trained on real farm data to benchmark growth and forecast harvest outcomes. Plans are underway to pilot the platform in Kenya through a collaboration with a local agritech partner, expected to be announced in 2026.
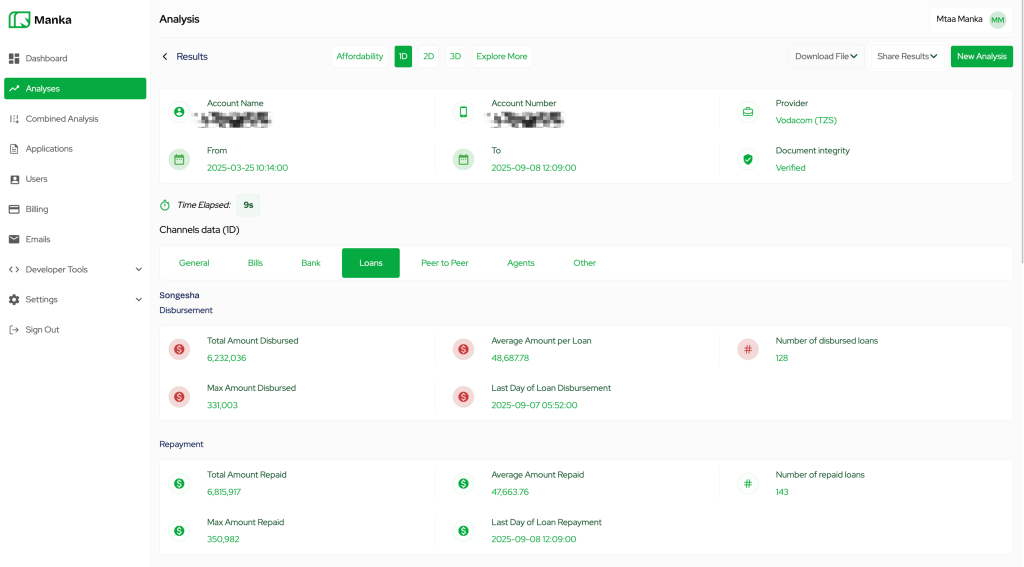
Black Swan: Unlocking Credit for the Unbanked through Alternative Data (Embedded Finance, Tanzania)
Founded by Derick Kazimoto and Alex Mkwizu, Black Swan is a fintech infrastructure provider enabling financial institutions to extend credit by leveraging alternative data sources. Acting as an embedded finance middleware, it allows digital lenders to instantly verify customer information-such as bank statements and utility bills-with user consent, facilitating more accurate credit risk assessments.
Employing AI and machine learning, Black Swan evaluates creditworthiness for individuals lacking traditional collateral, supporting services like Buy Now, Pay Later and device financing. For instance, a customer seeking to finance an iPhone 17 Pro Max can upload bank statements, which Black Swan’s AI verifies alongside credit bureau checks to pre-approve loans swiftly.
Currently active in Tanzania, Black Swan is piloting operations in Uganda, Kenya, Rwanda, and Malawi. A notable innovation in development is the “credit SIM,” a portable credit identity linked to a user’s phone number, enabling credit histories to move seamlessly across banks, lenders, and borders. The company operates on a revenue-sharing model, earning fees based on credit model performance after accounting for defaults.
Why Black Swan is a game-changer: Despite the proliferation of digital lending platforms, Africa faces a $100 billion credit gap, with over 500 million adults lacking formal identification to access loans. Black Swan’s approach bypasses traditional lenders by making financing data portable and accessible across platforms. Unlike competitors such as Jumo and Kunda, which rely heavily on telecom data, Black Swan remains independent of telco operators, enabling operation in markets without open banking frameworks. The startup’s model was recently validated by winning the MEST Africa Challenge 2025.
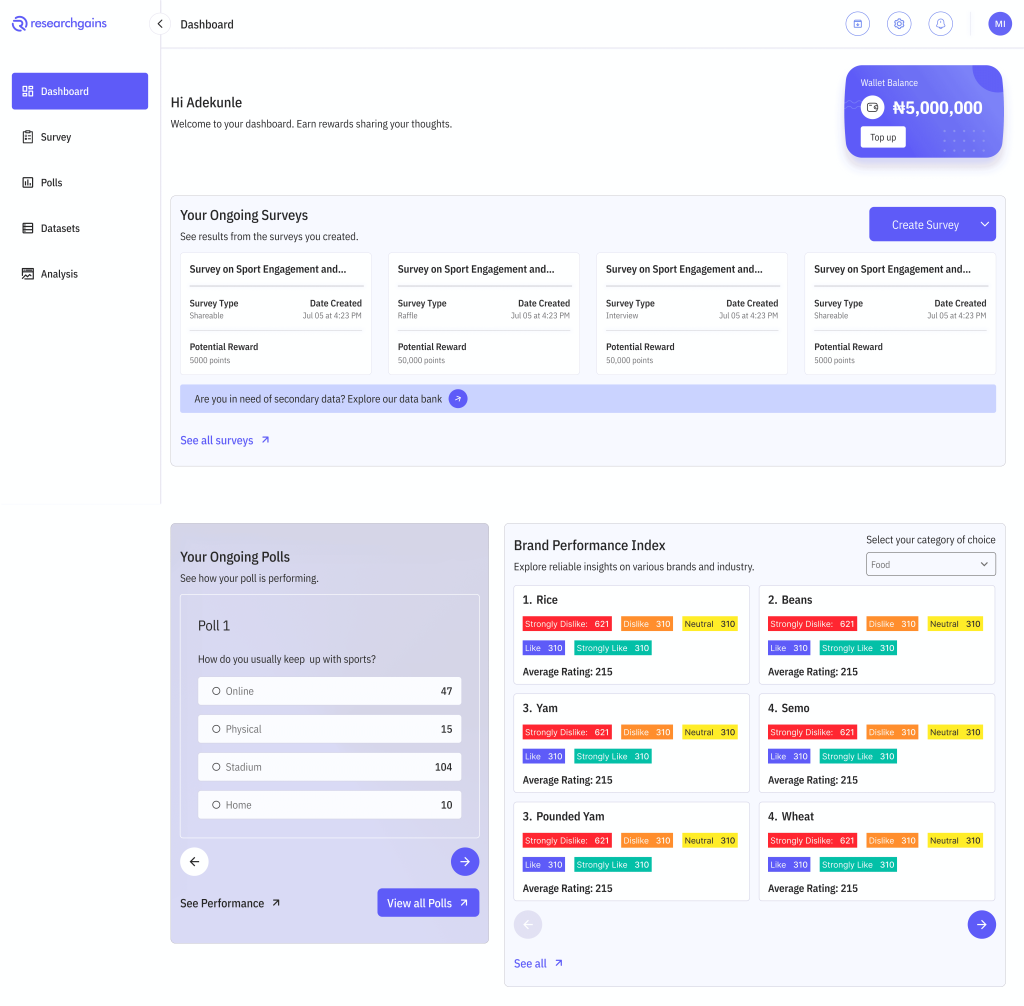
ResearchGains: Democratizing Data Collection for African Scholars (Data & Research, Nigeria)
Computer engineer Balogun Babaunde founded ResearchGains after encountering data integrity issues during his undergraduate research. The platform offers a digital infrastructure that enables research teams to collect, store, and analyze structured data efficiently. It connects researchers with verified respondents in real-time through an open data intelligence system.
Researchers can design qualitative (audio/video) or quantitative surveys targeting specific demographics using filters such as age, gender, location, employment, education, occupation, and ethnicity. To enhance inclusivity, the platform supports translations in nine languages, including Yoruba, Igbo, Hausa, Swahili, Zulu, Arabic, and Portuguese. Respondents earn redeemable points for survey participation.
Quality control is rigorous, employing National Identification Numbers (NIN) for identity verification, GPS tracking for location-based surveys, and response time analysis to detect fraudulent or rushed answers.
Pricing varies by package: the Student tier charges ₦200 (~$0.14) per respondent for up to 300 participants; Small Scale and Medium Scale packages cost ₦300 (~$0.21) and ₦250 (~$0.17) per respondent, accommodating up to 1,000 and 10,000 respondents respectively. ResearchGains claims access to a pool of 5 million respondents across diverse demographics.
Why ResearchGains matters: Africa contributes only 2% to global research output. By providing a platform with readily accessible African respondents and datasets, ResearchGains accelerates the continent’s research capacity. Compared to global tools like SurveyMonkey, which start at $35 per month, ResearchGains offers a cost-effective alternative tailored to African contexts, boasting over 400 local datasets to date.
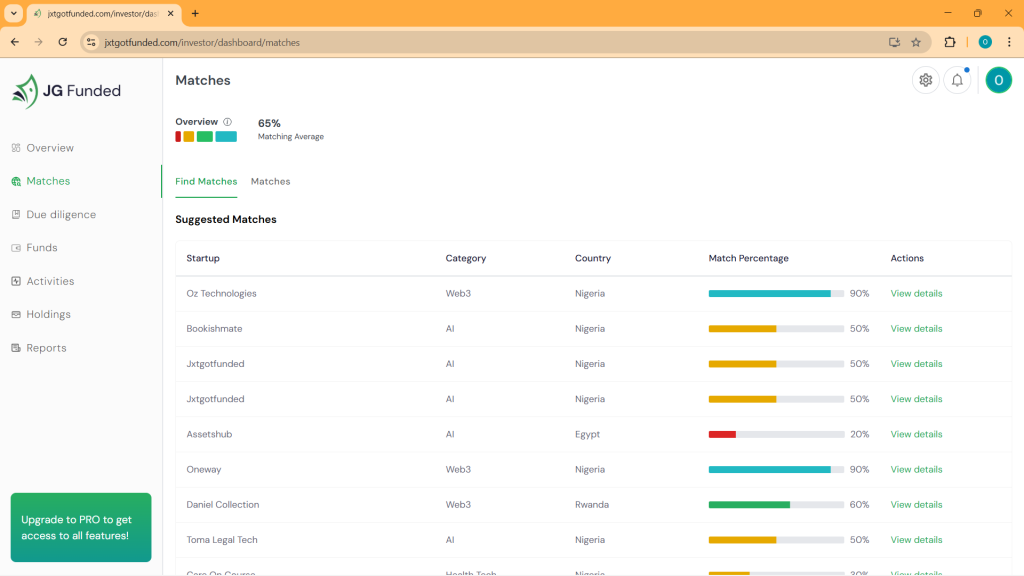
Jxtgotfunded: Accelerating Startup Fundraising with AI-Driven Matching (Networking, Nigeria)
Co-founded by Ozurumba Obinna and Wosu Ogechi, Jxtgotfunded is an AI-powered marketplace designed to streamline the fundraising journey for African startups. The platform addresses the dual challenges of limited startup visibility and prolonged investor due diligence caused by trust deficits.
Startups register on the web app, submitting details about their team, location, funding stage, traction, sector, and pitch decks. Investors specify their investment preferences, including ticket size, sectors, locations, and prior investments. The platform’s machine learning algorithm generates compatibility scores, helping investors focus on aligned opportunities. Matched parties can communicate directly within the app to manage deal flow.
Additional features include pitch deck analytics, document templates (e.g., NDAs), and market intelligence dashboards tracking funding trends. Upcoming AI agents will summarize financial documents, analyze projections, prepare due diligence reports, and generate sector-specific insights.
Jxtgotfunded currently operates on a success-fee basis, charging 2% to 5% commissions on closed deals, supplemented by partnerships with incubators and ecosystem data services. A subscription model unlocking premium features is planned. Since its MVP launch in October 2024, the platform has attracted approximately 500 startups.
Why Jxtgotfunded is noteworthy: In H1 2025, African startups raised $1.42 billion across 243 deals. Jxtgotfunded aims to expedite this process by reducing investor bias through AI matchmaking. Unlike platforms such as F6S, which use cohort models, or Startup List Africa, which serves as a directory, Jxtgotfunded offers a culturally attuned, trust-building approach tailored to Africa’s unique investment landscape, differentiating it from global counterparts like AngelList.

Maa: AI-Enhanced Maternal Care Tailored for African Mothers (Healthtech, Ghana)
Dr. Abena Jim-Annan and Aseda Addai-Deseh founded Maa to address critical gaps in maternal healthcare across Africa, including fragmented care continuity, emotional isolation, medication safety concerns, and limited access to specialists.
Maa is an AI-powered digital companion that supports mothers throughout the maternal journey. It allows users to store and synchronize clinical records-such as ultrasounds, lab results, and vaccination histories-and document pregnancy milestones, including scans and newborn photos, which the AI compiles into a digital keepsake for future sharing.
The app tracks vital signs to detect trends like rising blood pressure and features an intelligent medication management system that monitors side effects and sends dosage reminders. For example, if a user reports nausea after taking folic acid, the app alerts healthcare providers in real-time for timely intervention.
Additional functionalities include integrated telemedicine, multilingual support, community and peer mentorship groups organized by location or interest, and a family sync feature enabling partners to access health updates remotely.
Maa plans a freemium subscription starting at $2 per month, with revenue streams from corporate wellness packages, telemedicine fees, and hospital partnerships. Currently in testing, Maa has over 500 users on its waitlist and targets a Q2 2026 launch.
Why Maa is essential: In sub-Saharan Africa, only 64% of births are attended by skilled professionals, with maternal mortality rates at 536 per 100,000 live births. Maa’s culturally contextualized, data-driven approach aims to bridge this gap, offering tailored maternal care solutions grounded in African realities, unlike global maternal apps that may provide inaccessible recommendations.
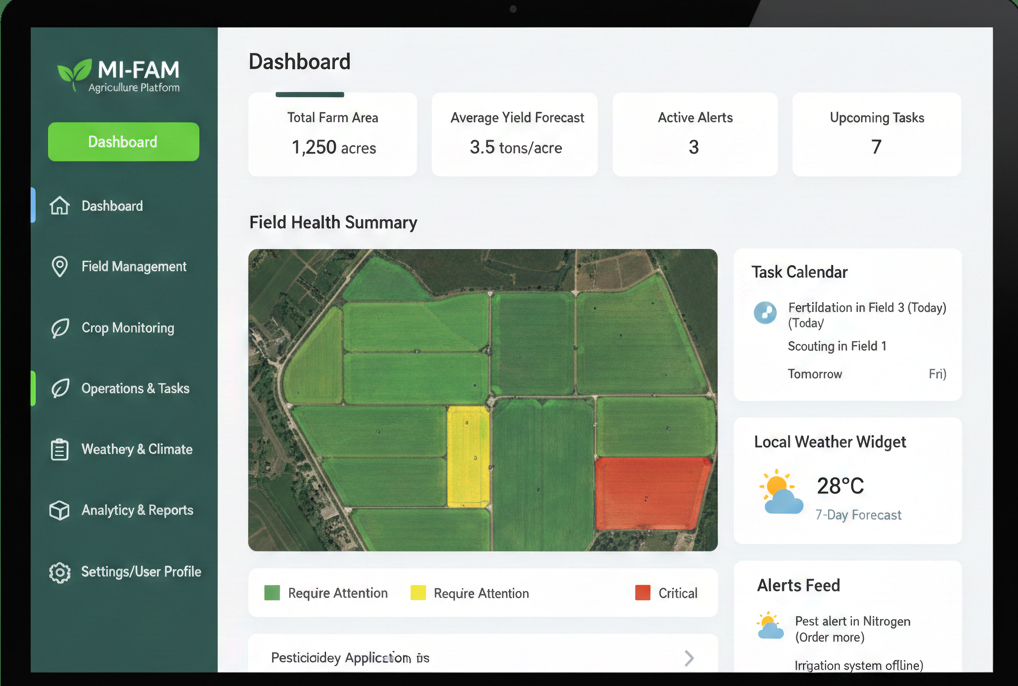
Mi-Fam: Empowering Sierra Leonean Farmers with AI Insights (Agritech, Sierra Leone)
Inspired by his mother’s farming challenges, N’fa Bolokada Umar created Mi-Fam to replace guesswork with data-driven decision-making for smallholder farmers in Sierra Leone. The platform combines AI diagnostics, weather forecasting, and a marketplace to enhance agricultural productivity and profitability.
Farmers can diagnose crop diseases and soil conditions by simply photographing plants; the AI analyzes images instantly without storing them, offering tailored advice such as removing infected leaves or applying specific fertilizers. Mi-Fam also predicts rainfall and temperature trends, recommending optimal planting and harvesting times.
To accommodate non-literate users, results are delivered via text or voice notes in local languages like Krio, Mende, and Temne. The integrated marketplace enables farmers to sell produce and trade equipment directly with buyers, eliminating costly intermediaries.
Currently in MVP testing, Mi-Fam offers premium subscriptions priced between SLE120 (~$5.22) and SLE250 (~$10.87), unlocking features like unlimited crop listings and an AI chatbot providing agricultural advice in local dialects.
Why Mi-Fam is impactful: Agriculture accounts for over 50% of Sierra Leone’s GDP. Mi-Fam addresses the sector’s reliance on intuition by delivering localized AI-powered tools that improve crop management and market access. Its focus on Sierra Leone-specific data ensures recommendations are highly relevant, positioning it as a transformative solution for smallholder farmers.
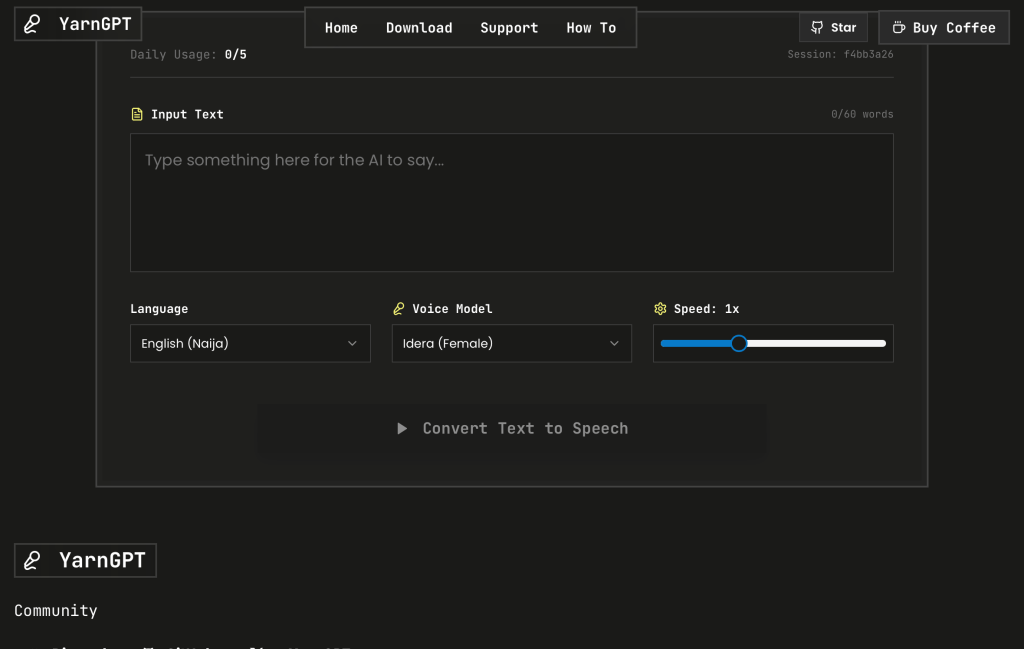
YarnGPT: Bringing Nigerian Accents to AI Voice Technology (AI, Nigeria)
Launched in 2025 by Saheed Ayanniyi, YarnGPT addresses the lack of Nigerian language and accent representation in existing text-to-speech AI models. Ayanniyi developed the platform by compiling datasets from Nigerian films to capture authentic speech patterns and intonations.
YarnGPT offers tools for video translation and text-to-speech synthesis, enabling creators to dub content into Nigerian languages such as Yoruba, Igbo, and Hausa within minutes. The platform also features a URL input tool that converts web content into audio narrated in Nigerian voices.
Developers can integrate YarnGPT’s API to embed Nigerian-accented or indigenous language speech into third-party applications. Additional features include a dialogue generator that produces multi-voice conversations with customizable pauses and speaker roles.
Why YarnGPT is pioneering: By focusing on local linguistic nuances, YarnGPT fills a critical gap in global AI voice technology, offering a homegrown alternative to Western-centric dubbing tools. This empowers African content creators to engage audiences in native languages, enhancing cultural relevance and accessibility.
That concludes our feature for today. Our next issue will be published on December 12, 2025. Know an innovative startup we should highlight? Submit your nomination here.